11 Different Types of Innoviation Meat Packaging
The primary purpose of meat packaging is to maintain the freshness, texture, color, and nutritional value of the meat while preventing microbial contamination and oxygen exposure, thereby extending the product’s shelf life.
With the development of technology, meat packaging has evolved from simple material selection to a comprehensive system that incorporates preservation techniques, hygiene standards, environmental considerations, and market trend analysis.
This article explores the various types of meat packaging, their functions, and their significance within the supply chain.
The Importance of Meat Packaging
Meat is an important source of nutrition for many people around the world.
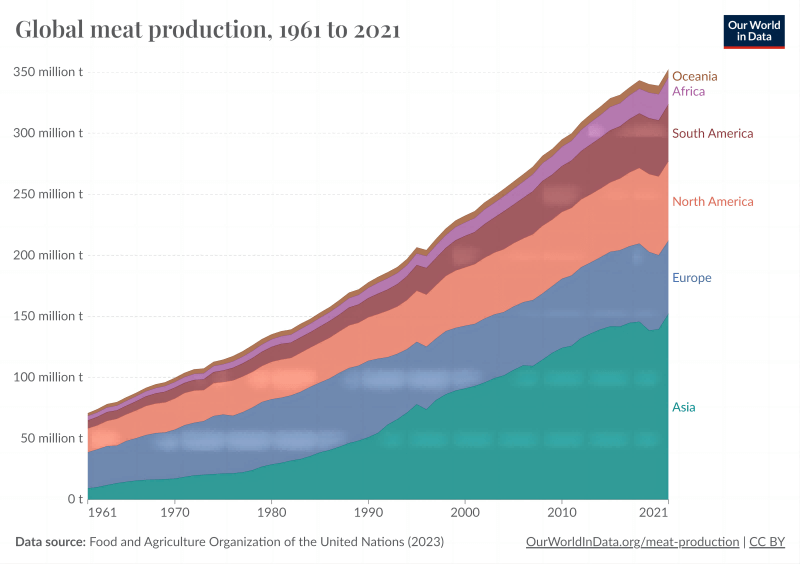
Global demand for meat is on the rise: over the past 50 years, meat production has more than doubled. Currently, global coal production exceeds 350 million tons annually.
The significant increase in demand for meat products, along with a notable shift in the structure of meat consumption towards high-quality meat products and fresh chilled meat, has become a trend in consumer development.
Therefore, research on meat packaging materials and packaging technology is essential.
1, Ensuring Meat Quality and Extending Shelf Life
Packaging cannot change the quality of meat products, but proper packaging can prevent microbial or external contamination, oxidation and rancidity of meat products, loss of moisture, and other factors that may lead to quality deterioration, thereby ensuring product quality.
2, Facilitating Transportation and Distribution
Meat products go through various processes such as transportation, storage, loading and unloading, and sales from the manufacturer to the consumer.
Packaging can protect meat products from damage due to collisions, making them easy to handle and manage during transport.
3, Promoting Sales
Selecting meat packaging materials and forms based on consumer demand can not only attract consumers but also enhance the product’s added value and competitiveness.
For example, attractive packaging design, convenient consumption methods, etc., can all contribute to boosting product sales.
11 Different Meat Packaging Types
Due to the different types of meat and meat products, their preservation and storage conditions vary. Therefore, there are many types of packaging materials used.
1, Cling Film
Cling film, also known as shrink wrap is typically a super-thin transparent film made of single-layer polyvinylidene chloride. This film has high oxygen and moisture barrier properties, high heat resistance, easy cutting during packaging, and strong adhesion for convenient use.
Shrink wrap helps maintain freshness and prevents dehydration but may not provide as much protection against punctures or tears compared to other methods.
Traditional meat products, fresh meats, semi-finished products, as well as cheese, vegetables, fruits, and other items sold in supermarket refrigerators are commonly packaged using this film.
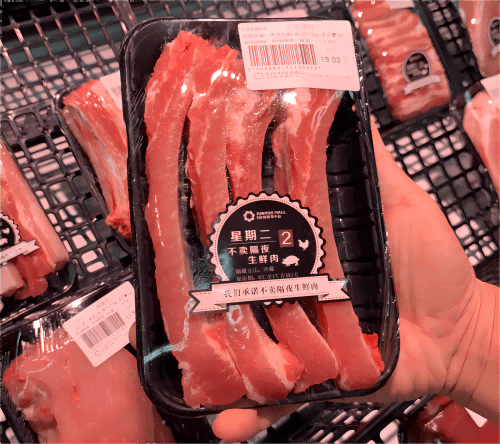
2, Tray Packaging
Chilled meats commonly sold in supermarkets are often placed on polystyrene trays covered with a transparent film.
2 types of transparent film materials for meat tray packaging:
- Cellophane
One side is coated with nitrocellulose to absorb moisture from the meat surface, promoting oxygen permeation to maintain color and reduce weight loss. Coating both sides with nitrocellulose is not suitable. - Polyethylene (PE)
Commonly known as PE, available in low-density, medium-density, and high-density forms. It has high oxygen permeability, especially low-density PE.Additionally, it exhibits good resistance to acids, alkalis, oils, and water vapor, making it suitable for packaging fresh meat. However, it lacks tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
The transparent film can be used to package pre-packaged cuts of meat, ground meat, marinated meats, chilled meats (such as refrigerated beef, pork, lamb, turkey, chicken, etc.), cooked meat products (such as char siu, bacon, meat pies, sausages, large hams, hot dogs), as well as cheese, fresh fish, and seafood.
3, Vacuum Packaging
Vacuum packaging refers to extracting all the air from the package and using packaging materials with extremely low oxygen permeability, preventing external oxygen from penetrating.
This process reduces the rate of oxidation and spoilage of fresh meat, ensuring its freshness.
After vacuum packaging, due to the absence of oxygen, meat products typically appear dark red, affecting their appearance. It’s commonly used for fresh meats, such as beef, pork, and poultry.
Upon unpacking and exposure to oxygen, chilled meats regain their fresh red color. Therefore, vacuum packaging is commonly used in hotels and supermarkets that require high-quality storage for extended periods.
The materials used in vacuum packaging include polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), which has excellent oxygen barrier properties and good shrinkage, as well as polyester, polyamide, nylon, polyester film, and multilayer polyethylene materials.
PVDC is known for its superior oxygen and water vapor barrier properties among various film materials, but its major drawback is its poor heat sealing capability.
Polyester exhibits strong tensile strength and flexibility.
Nylon has good oxygen barrier properties, is resistant to heat and cold, and has strong mechanical properties, but it has a high water vapor transmission rate and is expensive.
Therefore, it is often used in multilayer composite forms for vacuum packaging of fresh meat.
4, Modified Atmosphere Packaging (MAP)
Modified atmosphere packaging (MAP), also known as gas flushing packaging or gas exchange packaging, involves removing the air inside the packaging bag and then filling it with a certain proportion of nitrogen, carbon dioxide, and oxygen gases.
This process reduces the possibility of oxygen permeation to the minimum level, inhibiting the growth and reproduction of microorganisms, and thereby extending the shelf life of the product.
In the case of chilled fresh meat, MAP can also help maintain the color of the meat. It is often used for packaged meats like sausages and deli meats.
5, Vacuum shrink packaging
Vacuum shrink packaging refers to placing the product in a vacuum-sealed bag and then heating it to tightly wrap the product, creating a vacuum by removing air from the package.
This process ensures a tight and secure seal by conforming the packaging material closely to the shape of the product.
This method is commonly used for packaging various foods, electronic products, and other items to maintain freshness, prevent spoilage, and extend shelf life.
The main difference between vacuum shrink packaging and vacuum packaging lies in their application scope.
Shrink packaging is primarily used for products requiring moisture-proof film wrapping. Vacuum packaging, on the other hand, is mainly applied to food items requiring inhibition of bacterial growth, oxidation prevention, and resistance to mold and spoilage.
In principle, shrink packaging involves heating the shrink film to tightly adhere to the product, achieving moisture-proofing while enhancing product aesthetics.
Large cuts of meat can be packaged using vacuum shrink packaging, offering benefits such as reduced bag breakage rates and prevention of juice leakage during vacuum sealing.
Vacuum shrink treatment not only inhibits surface bacteria growth on chilled meat but also prevents secondary contamination, effectively extending shelf life.
Compared to modified atmosphere packaging, vacuum shrink packaging offers convenient transportation and lower packaging costs.
6, Aluminum Foil
The packaging materials for frozen meat must not only prevent the permeation of oxygen and water vapor to avoid fat oxidation and spoilage but also be able to withstand drastic temperature changes. They should shrink or expand accordingly during freezing or thawing operations.
Aluminum foil can be laminated with other materials to create flexible packaging used for packaging frozen foods, and it can also be formed into various shapes of semi-rigid packaging containers for packaging meats or ready-to-eat foods.
It has excellent resistance to water vapor and gas permeability, but its shrinkage and heat-sealing properties are relatively poor.
7, Meat Packaging Bags
Plastic film composite materials, such as nylon with polyethylene (PE), polyethylene with polyester film, low-density polyethylene (LDPE), and polypropylene (PP) coated with polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC), are commonly used as multilayer composite packaging materials for packaging hamburgers, steaks, etc. These are then placed in wax-coated cardboard boxes for freezing storage.
8, Meat Product Packaging
To maintain the quality of processed meat products, the selection of packaging materials needs to consider the characteristics of their production, processing, storage, and consumption methods.
There are many packaging materials for meat products, commonly divided into natural and artificial casings.
- Natural casings
Natural casings are mainly processed from the small intestines, large intestines, and bladders of pigs, cattle, and sheep, with pig intestines and sheep intestines being the most commonly used.The advantages of natural casings include good toughness, solidity, and the ability to withstand tension and heat treatment during processing. They also have the property of shrinking and expanding.
However, the disadvantages include uneven thickness, high cost, limited availability, and unsuitability for large-scale automated production.
- Artificial casings
Artificial casings include collagen casings, cellulose casings, and plastic casings.The advantages of artificial casings include standardized specifications, convenient processing, suitability for large-scale production, and the ability to preserve product flavor, extend shelf life, and reduce shrinkage. Currently, artificial casings are widely used worldwide.
9, Retort Pouch
Cooked meat products such as sauce, and ready-to-eat meals widely use retort pouches.
Retort pouches typically consist of several layers of flexible materials such as polyester, aluminum foil, nylon, and polyethylene, such as PET/NY/AL/RCPP.
These layers are chosen to provide barrier properties against moisture, oxygen, light, and other factors that can degrade food quality.
Retort pouches offer several advantages for packaging meat products. They are lightweight and flexible, making them easy to transport and store.
The ability to customize the packaging material and design allows for attractive product presentation and branding.
Additionally, retort pouches require less energy and resources to manufacture compared to traditional metal cans or glass jars, making them more environmentally friendly.
Retort pouches are commonly used for a variety of meat products, including pre-cooked meals, canned meats, ready-to-eat meals, and pet foods. They are particularly popular for camping, hiking, and other outdoor activities due to their lightweight and portable nature.
10, Canned Packaging
Meat products for ambient storage refer to those packaged in non-permeable materials, sterilized at temperatures above 121 degrees Celsius, and capable of being distributed at room temperature with a shelf life of over 6 months.
Materials suitable for this type of packaging must be non-permeable and able to withstand high-temperature sterilization.
Common materials used for meat product packaging include tin cans, aluminum foil, composite bags, glass jars, and polyvinylidene chloride (PVDC) films.
- Tin cans are made of tin plates. They are mainly used for packaging meat cans, such as canned luncheon meat, canned fish, etc. Products packaged in this way generally have a shelf life of over 1 year at room temperature.
- Aluminum foil containers are formed by stamping aluminum foil. They are mainly used for canned meat products.
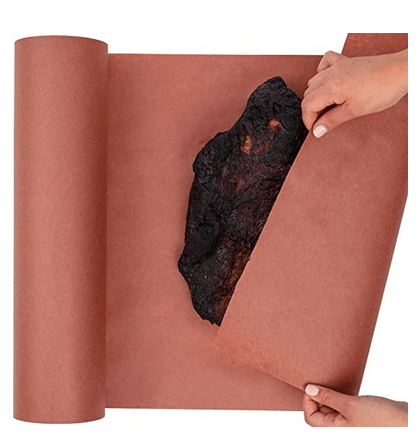
11, Butcher Paper
Butcher paper, also known as butcher’s paper or kraft paper, is a type of thick, sturdy paper that is commonly used in the food industry, particularly in butcher shops and meat packaging.
Butcher paper is typically made from unbleached kraft pulp, which gives it its characteristic brown color. It is known for its strength and durability, making it suitable for wrapping and protecting meat products.
One of the key features of butcher paper is its ability to allow meat to breathe. Unlike plastic or foil wrapping, butcher paper allows air to circulate the meat, which can help prevent the buildup of excess moisture and reduce the risk of bacterial growth.
Butcher paper is also popular for use in barbecue and smoking. It is often used as a wrapping material for brisket, ribs, and other meats during the cooking process. The paper helps retain moisture and flavor while allowing the meat to develop a desirable bark or crust.
The choice of packaging type depends on factors such as the type of meat being packaged, intended shelf life, transportation considerations, and consumer preferences. Each type has its advantages and limitations in terms of preservation, presentation, and sustainability.
Start With KDW
+86 13559233681(Wechat, Whatsapp)
No1, Anbian Rd, Torch High-Tech Zone (XiangAn), Xiamen, Fujian, China